Electronic signatures have become standard in business documentation. Contracts, invoices, consents, and corporate agreements are routinely signed as PDFs using tools such as Adobe Acrobat and similar readers. The process is fast, familiar, and widely accepted.
What is less visible is the legal strength of those signatures over time.
A document may look correctly signed today, but what happens if it is challenged months or years later? Can the signing date be proven beyond doubt? Can the document’s integrity be demonstrated to a judge, an auditor, or a forensic expert?
These questions are not theoretical. They sit at the heart of legal certainty in digital documentation, and they are precisely where time stamping plays a decisive role.
Table of contents
What makes a PDF signature legally robust?
Most PDF signing tools rely on digital certificates to identify the signer and bind their identity to the document. This provides a solid foundation, but it does not automatically guarantee long-term legal validity.
For an electronic signature to stand up legally, three elements must be demonstrable:
- Who signed the document
- What content was signed, without alteration
- When the signature was applied, with certainty and proof
The first two elements are usually covered by the certificate and the cryptographic seal. The third reliable proof of the exact signing time is where weaknesses often appear.
Without a qualified electronic time stamp, the signing date may rely on local system data or internal metadata that cannot be independently verified.

What is electronic time stamping?
Electronic time stamping is a trust service that certifies the exact date and time at which a digital document existed in a specific state.
The time stamp is issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP) acting as an independent third party. Once applied, it creates verifiable evidence that:
- the document existed at that precise moment
- its content has not been modified since
- the time reference comes from a trusted, certified source
This is not a technical detail. It is a legal safeguard.
Time stamping is widely used to support electronic signatures, certify digital transactions, seal audit logs, validate electronic invoices, and preserve evidence that must remain reliable over time.
The risks of signing PDFs without a qualified time stamp
Weak evidential value
Without a qualified time stamp, there is no independent proof of the exact signing moment. In legal proceedings or audits, this gap can be questioned.
Example: a contract marked as signed on “3 May” may be disputed if one party argues it was signed after a deadline.
Possibility of repudiation
A signer may deny having signed the document at a specific time. System clocks, time zones, or device configurations can be altered without leaving reliable evidence.
Reduced legal weight
Under the eIDAS Regulation, time stamping strengthens electronic signatures by anchoring them to a certified time. Without it, the signature may be treated as a simple electronic signature with lower probative value.
A common scenario: signing PDFs in Adobe Acrobat
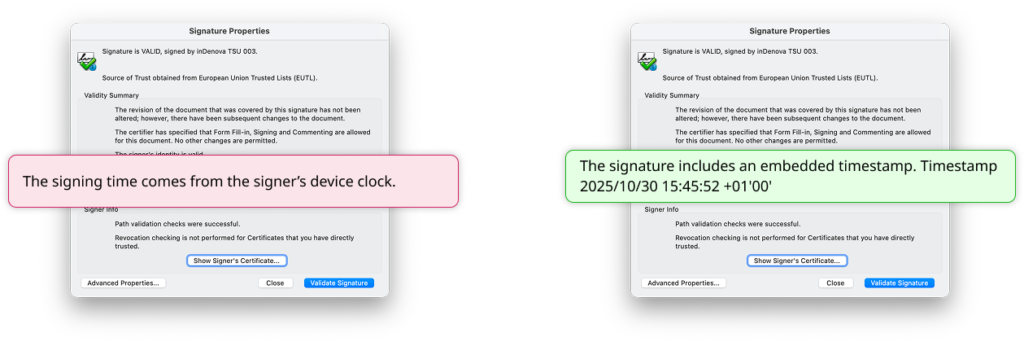
Signing a document in Adobe Acrobat with a digital certificate is a widespread practice. However, if no qualified time stamp is applied, the date and time associated with the signature are taken from the user’s device.
That timestamp is not issued, verified, or guaranteed by a trusted third party.
From a compliance perspective, this creates an evidential weakness that may only surface when the document is reviewed under scrutiny.
“From a compliance standpoint, signing PDFs without a qualified time stamp leaves room for evidential challenges in audits or legal disputes. Time stamping is essential to preserve legal validity over time.”
Compliance Department, Lleida.net
How to secure the legal validity of PDF signatures
Strengthening the legal value of a PDF signature does not require changing tools or workflows.
Qualified time stamping can be added to existing signing processes, including signatures created in Adobe and other PDF readers. Often, time stamping can be configured directly at the user level without technical development.
For organisations handling high volumes of documents or automated processes, time-stamping services are also available via API, allowing seamless integration into digital workflows.
The result is simple: the same signing experience, with significantly stronger legal certainty.
Time stamping that is self-managed, simple, and scalable
Easy user-level configuration
Most PDF readers allow time stamping to be configured directly at user level, without technical development or changes to existing workflows. Users only need the credentials provided by the qualified trust service provider, typically delivered securely by email.
This approach allows organisations to reinforce legal validity without disrupting daily operations.
HTTP protocol implementation for automated environments
For high-volume use cases or automated environments, qualified time stamping is also available via HTTP integration.
This enables organisations to integrate time stamping directly into back-office systems, document management platforms, or automated signing workflows.
Legal recognition under eIDAS and beyond
Qualified electronic time stamps are explicitly recognised under the eIDAS Regulation (EU No 910/2014).
A qualified time stamp benefits from a reinforced legal presumption:
- The indicated date and time are presumed accurate
- The integrity of the data is presumed
- The evidence is legally recognised across the European Union
Similar principles apply in multiple jurisdictions across Latin America and other regulated markets, making time stamping a key element for cross-border digital documentation.
International recognition
The legal validity of electronic signatures and time stamping is also recognised in multiple jurisdictions:
- Colombia: Law 527 of 1999 regulates the chronological stamping of data messages.
- Peru: Supreme Decree 052-2008 (Art. 33) establishes temporal certification for electronic documents.
- Dominican Republic: Decree 335-2004 develops Law 126-02 on electronic signatures.
- United Arab Emirates: Federal Law 46 of 2021 recognises integrity and authenticity requirements for digital documents.
As an authorised provider in these countries, Lleida.net offers services within the scope of ISO 27001 and ENS, and recognised by official bodies such as ONAC in Colombia and Indecopi in Peru as a value-added service.
Why time stamping matters in the long term
Digital certificates expire. Cryptographic standards evolve. Systems are replaced.
Documents, however, often need to remain valid for years: contracts, invoices, corporate records, regulatory evidence. Without a trusted temporal anchor, their legal value may erode over time.
A qualified electronic time stamp fixes the document in time. It preserves its evidential value even if the signer’s certificate has expired or the signature is examined long after it was applied.
Do not leave legal certainty to chance.
Buy a time stamp and sign with long-term legal confidence.
